What Causes Mouth Cancer?
As a trusted dentist, we’ve encountered various oral health issues, among them, mouth cancer remains one of the most concerning due to its severity and potential consequences. Understanding what causes mouth cancer, its symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for both prevention and early detection. At Oadby Dental Clinic, we’ll delve into the intricate details of mouth cancer from a dental perspective, so you can keep a watch out for those early signs and ensure mouth cancer detection early.
What Causes Mouth Cancer?
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, can arise due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
The primary risk factors include:
1. Tobacco Use
Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using smokeless tobacco significantly increases the risk of developing mouth cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco products damage cells in the mouth, leading to mutations that can trigger cancerous growths.
2. Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption is another leading cause of mouth cancer. Alcohol irritates the cells lining the mouth, making them more susceptible to cancerous changes. When combined with tobacco use, the risk of developing mouth cancer dramatically increases.
3. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, have been linked to an increased risk of mouth cancer. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, potentially leading to cancerous growths.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting oral hygiene practices can contribute to the development of mouth cancer. Poor oral hygiene allows bacteria to accumulate, leading to chronic inflammation and cell damage. Over time, this can increase the risk of cancerous changes in the mouth.
5. Dietary Factors
A diet low in fruits and vegetables and high in processed foods may increase the risk of mouth cancer. Adequate intake of fruits and vegetables provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that help protect against cancerous growths.
What are the Symptoms of Mouth Cancer?
Recognising the symptoms of mouth cancer is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment.
Common signs and symptoms include:
1. Persistent Mouth Sores
Mouth ulcers or sores that fail to heal within a few weeks may be indicative of mouth cancer. These sores may bleed easily and can be accompanied by pain or tenderness.
2. Changes in Mouth Tissues
Any abnormal changes in the tissues of the mouth, including red or white patches, thickening or lumps, should be evaluated by a dentist or healthcare professional.
3. Difficulty Swallowing or Chewing
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or chewing, along with persistent throat pain or discomfort, can be symptoms of advanced mouth cancer.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden and unexplained weight loss may occur as a result of difficulty eating due to mouth pain or swallowing difficulties caused by mouth cancer.
5. Persistent Sore Throat
A persistent sore throat that does not improve with time or treatment warrants further investigation, as it could be a sign of underlying mouth cancer.
What is Cancer of the Mouth?
Cancer of the mouth refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, gums, floor of the mouth, and the roof of the mouth. These cancerous growths can invade surrounding tissues and, if left untreated, may spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious complications.
How Does Cancer of the Mouth Start?
The development of mouth cancer typically begins with genetic mutations in the DNA of cells lining the mouth. These mutations can be triggered by various factors, as aforementioned by tobacco use, alcohol consumption, HPV infection, and poor oral hygiene. Over time, these mutated cells can grow uncontrollably, forming cancerous tumours or lesions within the oral cavity.
How to Treat Mouth Cancer
Treatment for mouth cancer depends on various factors, including the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health.
Common treatment options include:
1. Surgery
Surgical removal of the cancerous growths is often the primary treatment for mouth cancer. This may involve removing part or all of the affected tissue, as well as nearby lymph nodes if the cancer has spread.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery to treat mouth cancer.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful medications to kill cancer cells or prevent them from multiplying. It may be used before or after surgery, or in combination with radiation therapy for advanced cases of mouth cancer.
4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy medications are designed to specifically target cancer cells while minimising damage to healthy tissues. These medications may be used in combination with other treatments for certain types of mouth cancer.
5. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy works by boosting the body's immune system to better recognise and destroy cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with other treatments for advanced mouth cancer.
Mouth Cancer Screening
Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in the early detection of mouth cancer. During a dental exam, your dentist will carefully examine your mouth, lips, tongue, and other oral tissues for any signs of abnormality or suspicious lesions. If any abnormalities are detected, further diagnostic tests, such as biopsies or imaging studies, may be recommended to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
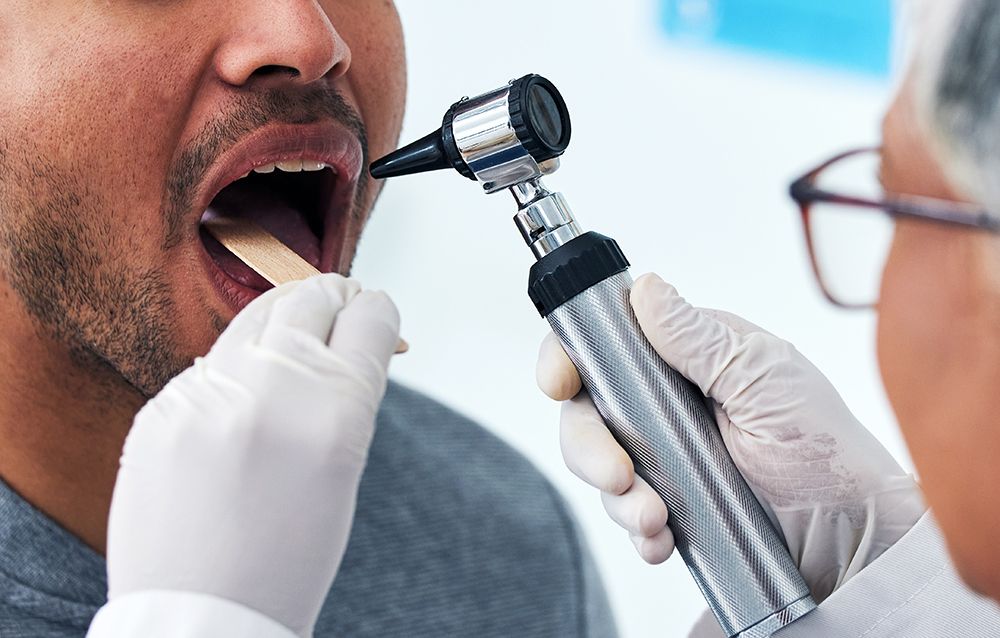
Mouth Cancer Screening Dentist
We’re committed to providing comprehensive oral health care to our patients, including routine mouth cancer detection in Leicester. During your dental visit, we will thoroughly evaluate your oral tissues for any signs of abnormality or potential cancerous lesions. Early detection is key to improving outcomes and increasing the chances of successful treatment for mouth cancer.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for mouth cancer is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals alike. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining good oral hygiene, and seeking regular dental care, you can reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer.



